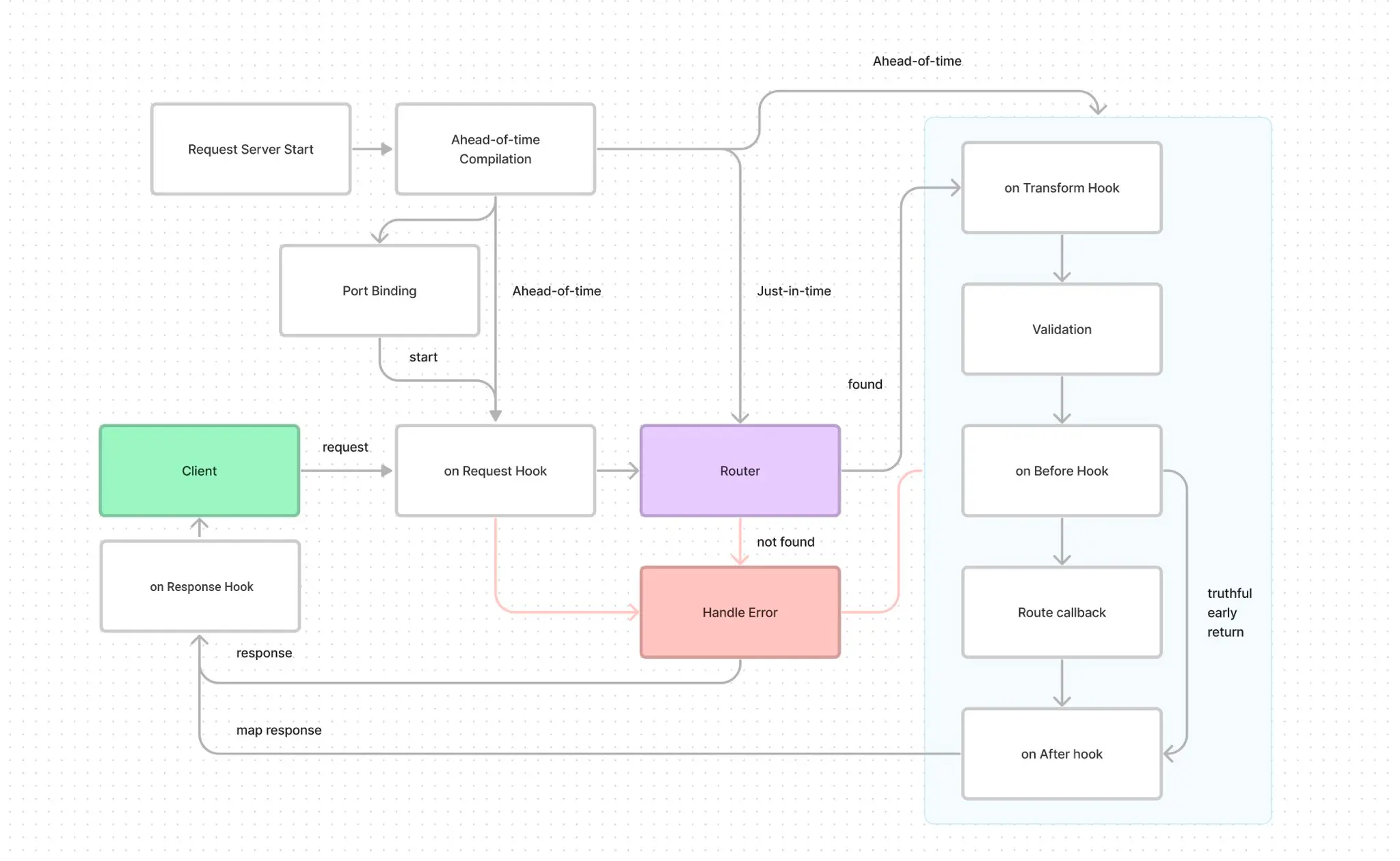
Trace
Performance is an important aspect for Elysia.
We don't want to be fast for benchmarking purposes, we want you to have a real fast server in real-world scenario.
There are many factors that can slow down our app - and it's hard to identify them, but trace can helps solve that problem by injecting start and stop code to each life-cycle.
Trace allows us to inject code to before and after of each life-cycle event, block and interact with the execution of the function.
Trace
Trace use a callback listener to ensure that callback function is finished before moving on to the next lifecycle event.
To use trace, you need to call trace method on the Elysia instance, and pass a callback function that will be executed for each life-cycle event.
You may listen to each lifecycle by adding on prefix follows by life-cycle name, for example onHandle to listen to handle event.
import { Elysia } from 'elysia'
const app = new Elysia()
.trace(async ({ onHandle }) => {
onHandle(({ begin, onStop }) => {
onStop(({ end }) => {
console.log('handle took', end - begin, 'ms')
})
})
})
.get('/', () => 'Hi')
.listen(3000)Please refer to Life Cycle Events for more information:
Children
Every events except handle have a children, which is an array of events that are executed inside for each life-cycle event.
You can use onEvent to listen to each child event in order
import { Elysia } from 'elysia'
const sleep = (time = 1000) =>
new Promise((resolve) => setTimeout(resolve, time))
const app = new Elysia()
.trace(async ({ onBeforeHandle }) => {
onBeforeHandle(({ total, onEvent }) => {
console.log('total children:', total)
onEvent(({ onStop }) => {
onStop(({ elapsed }) => {
console.log('child took', elapsed, 'ms')
})
})
})
})
.get('/', () => 'Hi', {
beforeHandle: [
function setup() {},
async function delay() {
await sleep()
}
]
})
.listen(3000)In this example, total children will be 2 because there are 2 children in the beforeHandle event.
Then we listen to each child event by using onEvent and print the duration of each child event.
Trace Parameter
When each lifecycle is called
import { Elysia } from 'elysia'
const app = new Elysia()
// This is trace parameter
// hover to view the type
.trace((parameter) => {
})
.get('/', () => 'Hi')
.listen(3000)trace accept the following parameters:
id - number
Randomly generated unique id for each request
context - Context
Elysia's Context, eg. set, store, query, params`
set - Context.set
Shortcut for context.set, to set a headers or status of the context
store - Singleton.store
Shortcut for context.store, to access a data in the context
time - number
Timestamp of when request is called
on[Event] - TraceListener
An event listener for each life-cycle event.
You may listen to the following life-cycle:
- onRequest - get notified of every new request
- onParse - array of functions to parse the body
- onTransform - transform request and context before validation
- onBeforeHandle - custom requirement to check before the main handler, can skip the main handler if response returned.
- onHandle - function assigned to the path
- onAfterHandle - interact with the response before sending it back to the client
- onMapResponse - map returned value into a Web Standard Response
- onError - handle error thrown during processing request
- onAfterResponse - cleanup function after response is sent
Trace Listener
A listener for each life-cycle event
import { Elysia } from 'elysia'
const app = new Elysia()
.trace(({ onBeforeHandle }) => {
// This is trace listener
// hover to view the type
onBeforeHandle((parameter) => {
})
})
.get('/', () => 'Hi')
.listen(3000)Each lifecycle listener accept the following
name - string
The name of the function, if the function is anonymous, the name will be anonymous
begin - number
The time when the function is started
end - Promise<number>
The time when the function is ended, will be resolved when the function is ended
error - Promise<Error | null>
Error that was thrown in the lifecycle, will be resolved when the function is ended
onStop - callback?: (detail: TraceEndDetail) => any
A callback that will be executed when the lifecycle is ended
import { Elysia } from 'elysia'
const app = new Elysia()
.trace(({ onBeforeHandle, set }) => {
onBeforeHandle(({ onStop }) => {
onStop(({ elapsed }) => {
set.headers['X-Elapsed'] = elapsed.toString()
})
})
})
.get('/', () => 'Hi')
.listen(3000)It's recommended to mutate context in this function as there's a lock mechanism to ensure the context is mutate successfully before moving on to the next lifecycle event
TraceEndDetail
A parameter that passed to onStop callback
end - number
The time when the function is ended
error - Error | null
Error that was thrown in the lifecycle
elapsed - number
Elapsed time of the lifecycle or end - begin